The Billion-Real Chat: A New Era for Banking in Brazil
Imagine a bank that has processed over one billion Brazilian Reals—the equivalent of roughly US$200 million. Now, imagine this financial institution has achieved this milestone without a single physical branch, no customer-facing website, and, most astonishingly, without its own dedicated mobile application.1This is not a hypothetical scenario from a distant future; it is the reality of
Magie, a Brazilian fintech that exists and operates almost entirely within the confines of the world’s most ubiquitous messaging platform: WhatsApp. This staggering achievement is more than just a headline-grabbing figure; it serves as a powerful proof-of-concept for a new paradigm in financial services, one that is quietly unfolding in the heart of Latin America’s largest economy.
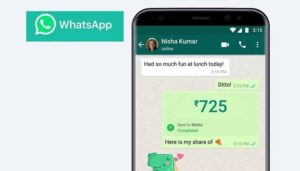
At the helm of this disruption is founder and CEO Luiz Ramalho, a figure whose background uniquely positions him to challenge the financial establishment. His creation, Magie, has stripped banking down to its most essential functions and embedded them into the daily conversational flow of its users. For an international audience, the concept is both simple and profound. Magie’s users can perform complex financial tasks with an ease that borders on the magical. Paying a boleto—a common Brazilian payment slip similar to an invoice—is as simple as taking a photo of it and sending it in a chat. Initiating an instant payment requires nothing more than sending a voice note with a command like, “Pay Maria R$50”. The platform handles the rest, providing confirmation within seconds.
This model represents a fundamental departure from the last decade of fintech innovation, which centered on building better, more user-friendly banking apps. Magie’s success suggests a deeper shift in consumer expectations. The R$1 billion milestone is not merely a vanity metric; it is the market’s definitive validation of a concept that can be described as “ambient finance.” This is the idea that financial services should not live in a destination app that users must consciously open, but should instead be seamlessly woven into the fabric of their existing digital lives. The platform’s rapid adoption and high transaction volume are a direct consequence of this strategy. Magie did not force users to learn a new behavior or download another piece of software. It simply inserted a high-value function—banking—into a pre-existing, universal behavior loop: chatting on WhatsApp.5 By meeting users exactly where they are, Magie has demonstrated that the path of least resistance is the most powerful catalyst for scale, offering a profound lesson in product strategy that extends far beyond the realm of finance.
The Architect of Disruption: The Vision of Founder Luiz Ramalho
To understand Magie’s audacious strategy, one must first understand the formidable background of its founder. Luiz Ramalho is not a typical startup founder. His career is a rare synthesis of experience from the highest echelons of traditional finance and the bleeding edge of technology and venture capital. He has navigated the demanding worlds of Investment Banking at Goldman Sachs and Real Estate Private Equity at The Blackstone Group, giving him an insider’s perspective on the global financial machine. This foundation in elite finance is complemented by a deep immersion in disruptive technology. Ramalho co-founded Fingerprints, one of the world’s most valuable collections of blockchain-based art, a venture that attracted backing from Silicon Valley royalty like Andreessen Horowitz (a16z) and Union Square Ventures (USV). As if that were not enough, he is also a Venture Partner at Canary, a prominent Latin American venture capital firm, giving him a panoramic view of the regional startup ecosystem.
This unique combination of credentials provides the context for his motivation in starting Magie. In his own words, Ramalho saw a clear opportunity to deploy artificial intelligence to correct the deep-seated “inefficiencies and misalignment between clients and institutions” that plague the Brazilian financial sector. His mission was not merely to create a slicker user interface but to tackle a fundamental structural problem he understood intimately from his time on both sides of the table—as a financier and a tech builder. His ultimate goal for Magie is not just to be a convenient transaction tool, but to evolve into a full-fledged, impartial financial assistant—an “equalizer” for the consumer. The long-term vision is for Magie to provide unbiased recommendations on complex financial products, such as advising a user on which bank offers the most favorable loan terms for their specific profile. This directly challenges the inherent conflict-of-interest model of traditional banks, which are primarily incentivized to push their own products, regardless of whether they are the best option for the customer. This ethos is even embedded in the company’s name, an homage to Lizzie Magie, the creator of the original version of the board game Monopoly, which was designed to illustrate the dangers of wealth concentration and promote a more equitable economic system.
This powerful combination of a founder with an impeccable resume and a grand, disruptive vision is precisely what attracts top-tier global investors. Ramalho’s background is, in venture capital parlance, Magie’s “unfair advantage.” It explains why a discerning U.S. venture fund like Lux Capital, known for backing contrarian ideas in science and technology, chose Magie for its first-ever investment in Brazil. Venture capitalists do not just bet on ideas; they bet on founders who can execute them at scale. A founder who has proven his mettle at Goldman Sachs, Blackstone, an a16z-backed startup, and a leading local VC firm is a uniquely de-risked proposition. The investment from Lux Capital was not a speculative punt on a clever concept; it was a calculated bet on a founder with a demonstrated ability to navigate complex financial regulations, build cutting-edge technology, and execute a massive, industry-altering vision.
The “Magic” Inside the Machine: Deconstructing Magie’s AI-Powered Service
The “magic” of Magie lies in its ability to make complex financial operations feel utterly simple. The user experience is designed to be as natural as chatting with a person. A user can forward a message containing a Pix key (a unique identifier for instant payments in Brazil) and Magie will understand the context and prepare the transaction. They can send a photo of a boleto, and Magie’s system will use optical character recognition (OCR) to extract the payment details and execute it. Or, they can simply send a voice message saying, “Magie, pay my phone bill,” and the AI agent will identify the correct bill and process the payment. This seamless interaction is a world away from the multi-step, often clunky process of navigating a traditional banking app.
What sets Magie apart from the simple, rule-based chatbots that have become common in customer service is its sophisticated AI engine. The platform is built on advanced Large Language Models (LLMs) and conversational AI, allowing it to understand natural language, interpret context, and discern user intent from a variety of unstructured inputs, including text, audio, and images. The objective is not to create a command-line interface where users must type precise commands, but a true “conversational agent” that can engage in a fluid, human-like dialogue to manage a user’s financial life.
However, this elegant front-end experience would not be possible without a robust and revolutionary piece of back-end infrastructure: Brazil’s instant payment system, Pix. Launched by the Central Bank of Brazil in 2020, Pix is a real-time payment network that allows for instantaneous, 24/7, low-cost money transfers between any participating financial institution. It has been a monumental success, processing nearly 42 billion transactions by 2023 and becoming the foundational rail upon which a new generation of fintech innovation is being built.15 Magie did not need to build its own payment network; it only needed to build the world’s best interface for the one that the government had already provided for everyone.
This architecture reveals Magie’s true strategic genius. The company’s business model represents the “Great Abstraction” of financial services. Magie is not, in essence, a bank; it is an interface layer. Its core technological innovation is not in creating new financial products but in abstracting away the immense complexity of using existing ones. The user is completely shielded from the underlying mechanics of OCR technology, API calls to the Pix network, and integrations with various banking partners. When a user wants to pay a bill, the traditional process involves finding their banking app, logging in with a password or biometrics, navigating to a “payments” section, choosing to scan a barcode or manually input numbers, confirming the transaction, and logging out. Magie’s process is simply: “open WhatsApp, send photo”. The number of steps and the cognitive load required are reduced by an order of magnitude. Magie’s true product is the mental energy it saves the user. This powerful abstraction is made possible by the convergence of three key technologies: the WhatsApp platform for ubiquitous distribution, the Pix API for flawless execution, and AI for intelligent translation and interpretation. Magie’s brilliance was in being the first to bundle these three powerful, independent components into a single, seamless, and profoundly simple consumer experience.
Why Brazil is the Ideal Launchpad for Conversational Banking?
Magie’s innovation, while technologically impressive, is also a product of its environment. The company’s explosive growth would be difficult to replicate elsewhere, as Brazil represents a unique “perfect storm” of cultural, technological, and regulatory conditions that have made it the ideal launchpad for conversational finance.
The first and most critical element is the absolute dominance of WhatsApp. In Brazil, the app is more than just a communication tool; it is the country’s de facto digital operating system. It is installed on an estimated 99% of smartphones, and 93% of users open it daily, spending over 24 hours a month on the platform—significantly higher than the global average.5 Brazilians affectionately call it “Zap” and use it for everything from coordinating with family to conducting business. The official launch of WhatsApp Payments in Brazil, after initial regulatory hurdles, further legitimized the platform as a secure channel for financial transactions, paving the way for services like Magie to build upon it.
Secondly, Brazil has undergone a profound fintech revolution, largely catalyzed by the “Nubank Effect.” The monumental success of the neobank Nubank, which went public in a blockbuster IPO in 2021, accomplished two crucial things for the ecosystem. First, it conditioned tens of millions of Brazilians to trust and enthusiastically adopt digital-first banking solutions, breaking the long-held dominance of the country’s traditional incumbent banks. Second, it firmly placed Brazil on the map for top-tier global venture capitalists, signaling the market’s maturity and immense potential, which in turn eased the fundraising path for subsequent startups like Magie. This is situated within a booming market; Brazil’s fintech sector is the largest in Latin America and is projected to grow from US 4.73 billion in 2024 to US 17.58 billion by 2033.
Finally, Magie is riding the powerful wave of conversational commerce. This is not a niche trend in Brazil; it is a mainstream economic force. The market for commerce conducted via messaging apps was valued at over US 10 billion in 2023 and is forecast to more than double to over US2 5 billion by 2028. A remarkable 79% of Brazilian WhatsApp users have already messaged a brand, and 62% have completed a purchase directly within the app. This cultural comfort with “chat-shopping” means that using WhatsApp for financial services is not a strange or intimidating leap for consumers; it is the next logical step in a behavior pattern that is already deeply ingrained.
These factors combine to create a unique incubation chamber for a model like Magie’s, born from a rare convergence of top-down and bottom-up innovation. The top-down enablers were deliberate, forward-thinking government actions. The Brazilian Central Bank proactively built the technical and regulatory infrastructure for the future of finance through the creation of Pix and the implementation of Open Banking frameworks. Simultaneously, bottom-up adoption was driven by private-sector disruptors. Nubank rewired consumer behavior and trust, while WhatsApp became the default digital public square. Magie could not exist without all of these pillars in place. Without Pix, the service would be clunky and slow. Without the trust cultivated by Nubank, users would be too skeptical to adopt a bank in a chat app. And without the ubiquity of WhatsApp, the frictionless distribution model would be impossible. Magie’s success is therefore a direct result of its founders’ acuity in building a product that sits at the precise intersection of these powerful, independent market forces. Brazil is not just a market for Magie; it is a necessary component of its very DNA.
Magie’s Strategy for Growth and Security
With a groundbreaking product and a fertile market, Magie’s strategy is now focused on two of the most critical elements for any fintech: growth and trust. The company’s go-to-market playbook is being executed in clear, deliberate phases.
The first phase is centered on Freemium-led user acquisition. Currently, Magie’s core services are free for individual users. This approach has allowed the company to rapidly acquire an initial user base—growing to over 12,000 clients shortly after its launch in early 2024—and, crucially, to gather vast amounts of interaction data. This data is the lifeblood of its AI engine, enabling the continuous refinement of its language models and improving the platform’s ability to understand and execute user requests with ever-increasing accuracy.
The second phase, the monetization strategy, is planned around a premium subscription model. The long-term vision is to charge a fee for access to Magie’s most advanced capabilities. This premium tier will leverage the platform’s AI to provide high-value, impartial financial advice and decision support, transforming Magie from a simple transaction tool into an indispensable financial co-pilot. This aligns with Ramalho’s goal of creating an “equalizer” that helps users navigate the complexities of the financial market.
Magie’s initial decision to target high-income individuals is a key part of this strategy. This is not a play for elitism but a shrewd market segmentation tactic. This demographic is typically less sensitive to price and more sensitive to the value of their time. They are the ideal beachhead market for a service that offers supreme convenience and time-saving benefits, making them the most likely early adopters of a future premium subscription.
Of course, for any financial service, the ultimate currency is trust. Magie has built its platform with security as a cornerstone. Every transaction requires authentication via a special six-digit PIN or the user’s phone biometrics (like a fingerprint) to prevent unauthorized activity.1 The company has also announced plans to strengthen its security infrastructure further by adding features like facial recognition. These measures are essential for operating within the framework of Brazil’s
Lei Geral de Proteção de Dados (LGPD), the country’s strict data privacy law, which is analogous to Europe’s GDPR and imposes significant obligations on any organization that processes personal data.
Interestingly, Magie’s model offers a counterintuitive security benefit that has resonated strongly with its user base. In testimonials, users have highlighted that they feel safer using Magie because it allows them to remove their traditional banking apps from their smartphones. In a country where street-level crime and phone theft are significant public concerns, this is a powerful value proposition. By using Magie, the smartphone is transformed from a vault containing the keys to one’s entire financial life into a simple terminal. The core access is protected by the Magie platform and its multi-layered security, externalizing the risk and reducing the potential damage from a physical theft.
| Metric | Detail |
| Founders | Luiz Ramalho (CEO), João Camargo |
| Concept | AI-Powered Financial Assistant on WhatsApp |
| Key Technology | Conversational AI (LLMs), Pix Integration |
| Total Funding | US$5.1 Million (Seed Round) |
| Lead Investors | Lux Capital, Canary |
| Key Milestone | > R$1 Billion in transactions processed |
| User Base | > 12,000 clients (as of Aug 2024) |
| Business Model | Freemium (Current) with planned Premium Subscription |
Can an AI in a Chat App Outsmart Traditional Banks?
In synthesizing the story of Magie, it becomes clear that it is more than just a clever novelty or a regional success story. It represents a potential blueprint for the next generation of financial services, signaling an evolutionary leap in how humans interact with their money. To fully appreciate its significance, it is useful to frame Magie’s emergence within the recent history of financial technology.
We can think of this evolution in three stages. Fintech 1.0 was the era of digitization, where traditional, incumbent banks like Bradesco and Itaú took their existing services and created websites and mobile applications for them. The underlying products and business models remained largely unchanged; only the channel of access was updated.
Fintech 2.0 was the era of the neobank, pioneered and perfected by companies like Nubank. These digital-first challengers built new banks from the ground up, free from the legacy infrastructure and cost structures of the incumbents. They disrupted the market primarily on the axes of lower fees, superior customer service, and a more intuitive user experience, capturing a massive and loyal customer base in the process.
Magie represents the dawn of Fintech 3.0. This is the era of “interface-first” or “ambient” finance. These models are radically asset-light. They do not require their own app, let alone a banking license. They exist as an intelligent, conversational layer that sits on top of existing platforms (like WhatsApp) and open financial infrastructure (like Pix and Open Banking APIs). Their core competency is not in holding deposits or underwriting loans, but in mastering the user experience and abstracting away all complexity.
The global implications of this model are profound. Magie’s success in Brazil provides a powerful template for other regions where the same key ingredients are beginning to converge: the ubiquity of a single messaging platform and the rise of government-mandated open finance initiatives. The question for the financial industry is no longer if artificial intelligence will fundamentally transform banking, but how. Magie’s answer—that it will do so by making the bank itself disappear into the background, fully integrated into the conversations that define our daily lives—is one of the most compelling and potentially prophetic visions for the future of finance worldwide.